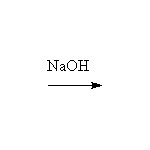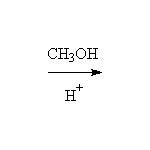Reactions of Ethers and Epoxides
You may use these summaries and problems but you may NOT download them for use at another site, nor may you charge for access to them. Copyright Linda M. Sweeting 1997
To synthesis of ethers or back to the main graphical reactions menu

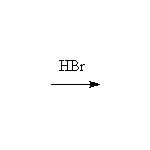 CH3CH2CH2Br +
CH3CH2CH2Br +
 +
+
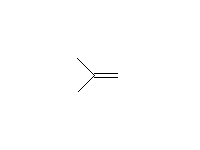
Both SN2 and SN1 (and E1) reactions occur, depending on the substrate. If a phenyl ether is used, SN2/SN1 reaction occurs only on the alkyl carbon, leaving phenol as a product.
McMurry 18.5, Fessenden 8.3, Schmid 13.9
Epoxides
These strained ethers are very easy to make but very reactive toward nucleophiles; think of them as spring-loaded ethers. One enantiomer is shown for each starting material and product.
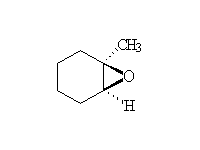
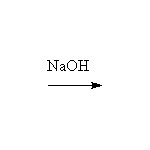
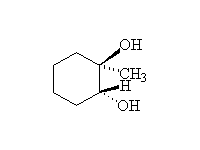
Stereospecific! Base-catalyzed ring opening is by SN2 at the less substituted carbon.
McMurry 18.8, Fessenden 8.4, Schmid 13.12

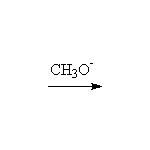
Stereospecific! Base-catalyzed ring opening is by SN2, at the less substituted carbon. Note that other nucleophiles , such as thiols, thiolates, cyanide, also will open the ring.
McMurry 18.8, Fessenden 8.4, Schmid 13.12


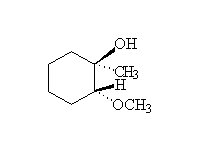
Stereospecific, giving the enantiomer of that shown. Acid catalyzed ring opening occurs via SN1 on the protonated epoxide, on the more substituted carbon but with strong preference for the backside.
McMurry 18.8, Fessenden 8.4, Schmid 13.12

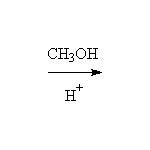
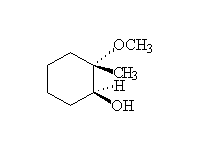
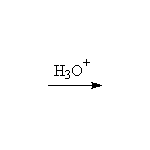
Stereospecific, as shown. Acid catalyzed ring opening occurs via SN1 on the protonated epoxide, on the more substituted carbon but with strong preference for the backside.
McMurry 18.8, Fessenden 8.4, Schmid 13.12
To synthesis of ethers or back to the main graphical reactions menu
Last update Feb. 1, 1999

 CH3CH2CH2Br +
CH3CH2CH2Br +
 +
+