Except for acid-base reactions, products are shown after neutralization in aqueous solution.
From the conjugate acid
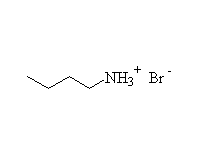
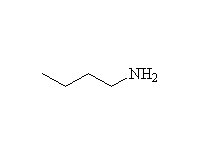 + H3O+
+ H3O+
McMurry 24.6, Fessenden 18.4A, Schmid 22.5
Note the universal use of pKa in organic chemistry.
By nucleophilic substitution
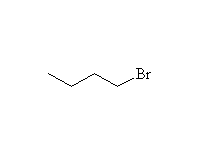


 +
+
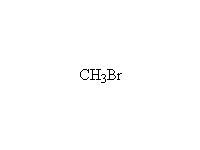
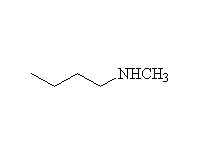

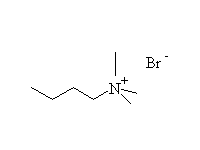
The reaction is hard to control, because the products are at least as reactive; it works well for making amino acids from halo acids because the product is the conjugate acid of the amine (the carboxylic acid protonates it)
Mechanism!
McMurry 11.2, 11.5, 24.6, Fessenden 18.4A, Schmid 22.8
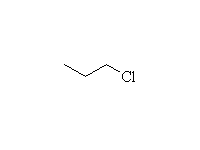 +
+
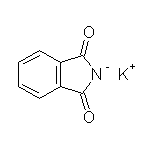
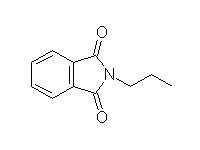

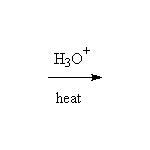
Other reagents for hydrolysis: NaOH, H2O and heat.
You have learned the mechanisms for the steps of this synthesis: SN2, amide hydrolysis
McMurry 24.6, Fessenden 18.4A, Schmid 22.9 (Gabriel synthesis), 16.8
By reduction of other nitrogen compounds
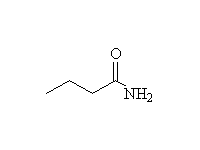
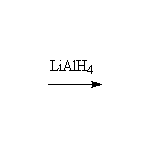

Other reagents: NaBH4
Nitrile reduction is essentially the same.
McMurry 24.6, Fessenden 18.4B, Schmid 16.12, 16.15
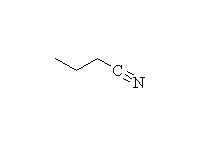
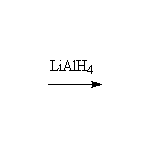

McMurry 24.6, Fessenden 18.4B, Schmid 22.10, 12.4
Azide ion (N3- is similar to CN-, except that the synthesis of cyanide (nitrile) from halide adds a carbon to the chain.
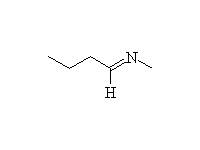
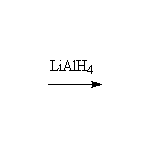

Fessenden 18.4B, Schmid 22.10
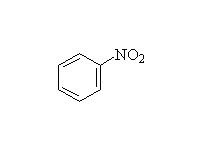
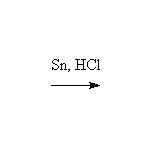
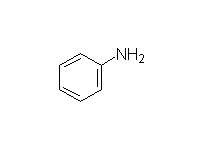
Fessenden 12.3, 18.4B, Schmid 22.10
By addition to alkenes
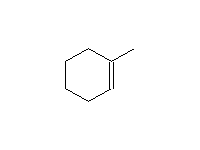
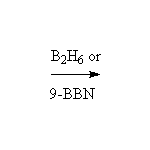
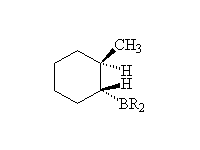

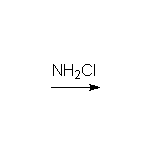
Reference McMurry 7.5 Schmid 22.11
Back to the Graphical Reactions Menu
Last update February 1999.