As Bronsted bases
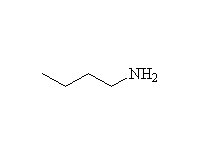
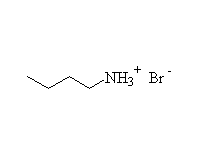
Note that the pKa of the conjugate acid is most commonly used instead of pKb of the amine.
McMurry 24.6, Fessenden 18.6, Schmid 22.5
As nucleophiles - with sp3 carbon
 +
+
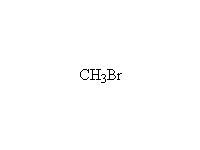
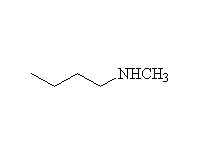

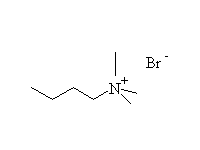
Reaction is very hard to control
Mechanism!
McMurry 11.2, 11.5, 24.6, Fessenden 18.7, Schmid 22.8
As nucleophiles - with sp2 carbon
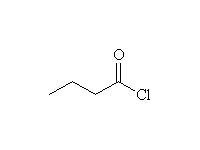
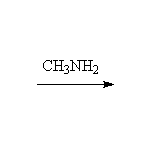
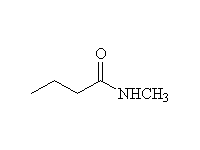 + HCl
+ HCl
Anhydrides react similarly yielding one mole of the carboxylic acid instead of HCl
Mechanism!
McMurry 21.7, 24.7, Fessenden 18.7, Schmid 16.5, 22.18
To other reactions of acid chlorides
 +
+
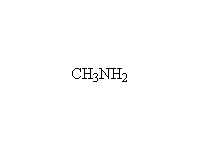
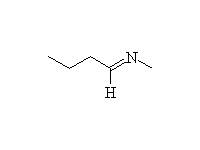
An imine. Anhydrous conditions needed. This reaction works better if the amine has an electron-withdrawing group to make it less basic. In that case, the acid protonates the carbonyl, making it more reactive. Examples include substituted hydrazines (NH2NHR), where the other nitrogen makes the one on the left less basic.
Mechanism!
McMurry 23.12, Fessenden 13.5A, Schmid 14.13 - 14.15
To other reactions of aldehydes and ketones
 +
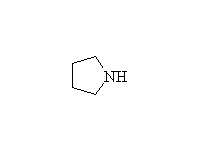
+ 

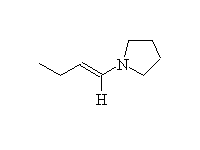
An enamine, which reacts like an enolate. Anhydrous conditions needed.
McMurry 23.12, Fessenden 13.5B, Schmid 14.13, 17.14
To other reactions of aldehydes and ketones
Oxidation

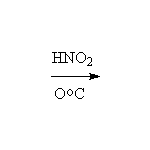
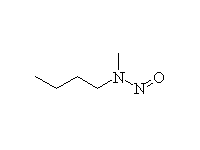
Carcinogenic!
Fessenden 18.8, Schmid 22.14
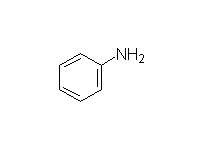
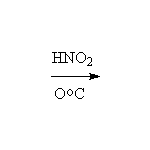
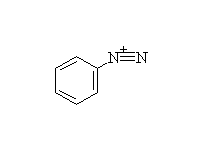
McMurry 24.8, Fessenden 12.3A, Schmid 22.14 - 22.15
Diazonium salts are very useful in synthesis.

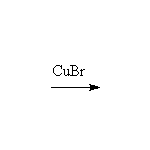
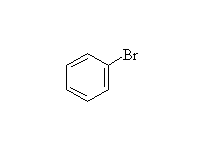

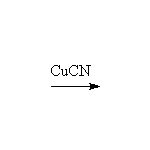
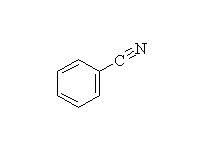

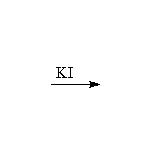
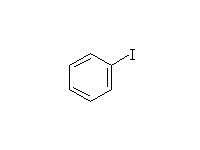

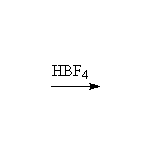
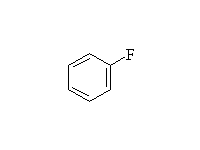

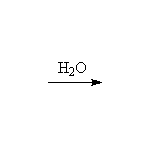
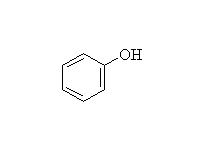

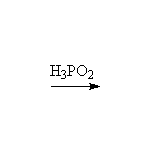
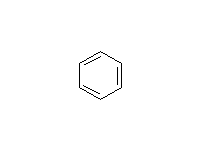
 +
+ 
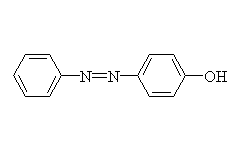
McMurry 24.8, Fessenden 12.3AB, Schmid 22.16 - 22.17
Back to the Graphical Reactions Menu
Last update February 1999.