- an absolute value for the oxidation state cannot be determined.
- only the changes in oxidation state during a reaction are important, so the
absolute value isn't needed.
- Elements other than carbon are assigned their normal oxidation state: H: +1; O:
-2; halogens: -1; and as a consequence OH: -1. There are easily recognized
situations where these elements are known to have other oxidation states:
hydrides such as LiAlH4 (H: -1), peroxides such as H2O2 (O: -1), or the elements (Cl2, H2, O2: 0).
- Once the particular carbon of interest is chosen (the one that is changed during
the reaction), all other carbons are assigned an oxidation state of 0 (even if you
know otherwise)! The oxidation state of the carbon of interest is then calculated
by the method used for an inorganic element like Mn in KMnO4 above.
Examples:
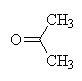
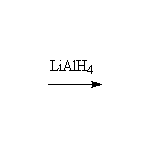
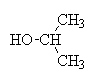 + Li+ + Al+3
+ Li+ + Al+3
Acetone carbon oxidation states:
| Carbon number | Attached atoms | Sum of oxn nos of attached atoms | C oxidation state |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 3H, 1C | 3(+1) + 1(0) = +3 | -3 |
| 2 | 2C, 1O | 2(0) + 1(-2) = -2 | +2 |
| 3 | 3H, 1C | 3(+1) + 1(0) = +3 | -3 |
2-Propanol carbon oxidation states
| Carbon number | Attached atoms | Sum of oxn nos of attached atoms | C oxidation state |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 3H, 1C | 3(+1) + 1(0) = +3 | -3 |
| 2 | 2C, 1H, 1OH | 2(0) + 1(+1) + 1(-1) = 0 | 0 |
| 3 | 3H, 1C | 3(+1) + 1(0) = +3 | -3 |
BALANCING EQUATIONS
 + H2O
+ H2O 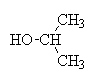 + LiOH + Al(OH)3
+ LiOH + Al(OH)3
The Li: +1, Al: +3, O: -2 and the CH3's are unchanged by this reaction. Changed are C-2 and H. The half reactions, balanced, are:
 + 2e- + 2 H+
+ 2e- + 2 H+
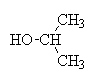
 + LiAlH4 + 4 H+
+ LiAlH4 + 4 H+ 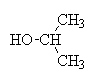 + Li+ + Al+3
+ Li+ + Al+3
 + LiAlH4
+ LiAlH4 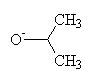 + Li+ + Al+3
+ Li+ + Al+3
OTHER USES
 CH3-CH2OH
CH3-CH2OHIn this case, the computation indicates a reshuffling of electrons within the molecule, making the two carbons different, but no overall oxidation. This should not be surprising, since water is not easy to oxidize or reduce (sodium metal can reduce it partially to H2).
ORGANIC ENRICHMENT, L. M. SWEETING, 1993, 1997