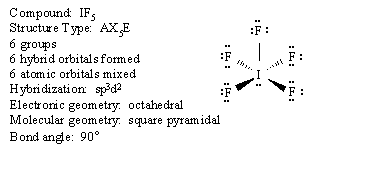
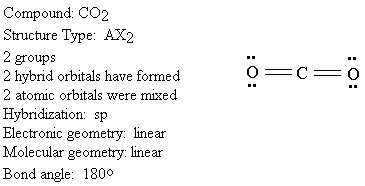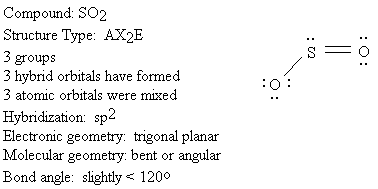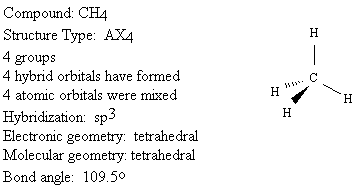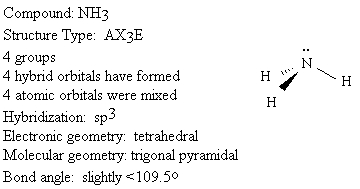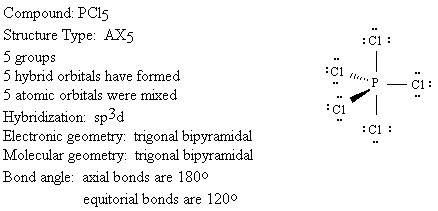We will use the following key to describe the shapes of molecules.
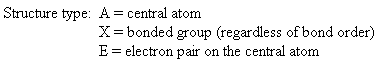
Groups: sum of X and E (number bonded groups and electron pairs)
Hybridization: which atomic orbitals were mixed
Electronic geometry: shape based on regions of electron density
Molecular geometry: shape based on location of nuclei
Bond angle: angle between X-A-X (central atom and two bonded groups)
We will look at each structure type in turn. An example of each will be given.
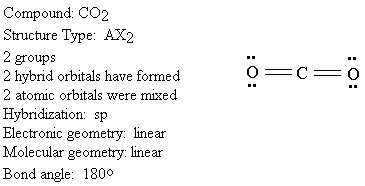

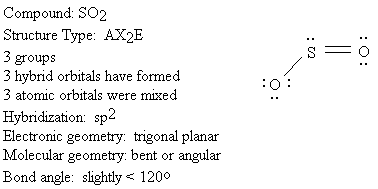
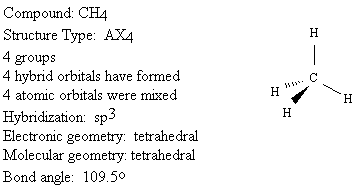
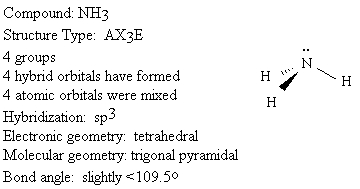

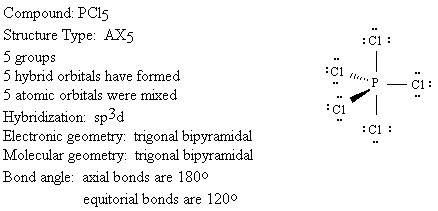





Created With HTML Assistant Pro - 05/11/2001
© Copyrght, 2001, L. Ladon. Permission is granted to use and duplicate these materials for non-profit educational use, under the following conditions: No changes or modifications will be made without written permission from the author. Copyright registration marks and author acknowledgement must be retained intact.